Hemorrhage control is a crucial aspect of first aid and emergency care. It refers to the process of stopping bleeding in order to prevent serious injury or death. In emergency situations, quick action is vital in order to prevent further harm to the patient. Hemorrhage control can be achieved through the use of various devices and techniques, including tourniquets, compression bandages and dressings, and hemostatic agents. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of hemorrhage control in emergency situations and the role of the bystander in providing first aid for bleeding. We will also discuss the different types of bleeding control devices and how to use them effectively; instead of just filming it! Finally, we will touch on the importance of proper training and practice in order to be prepared to handle emergencies with confidence.
Table of Contents
The consequences of uncontrolled bleeding
The risk of death from uncontrolled bleeding is significant, especially in emergency situations. Bleeding can quickly become life-threatening if it is not stopped in a timely manner. This is especially true if the bleeding is severe or if it is occurring in a vital organ or artery. If bleeding is not controlled, the loss of blood can lead to shock, organ damage, and ultimately death.
In addition to the risk of death, uncontrolled bleeding can also have long-term health impacts. For example, if bleeding is not controlled, it can lead to the formation of blood clots, which can cause further complications such as stroke or deep vein thrombosis. Uncontrolled bleeding can also cause scarring and long-term disability, particularly if it occurs in a joint or other important area of the body. Overall, it is essential to control bleeding as quickly as possible in order to prevent serious consequences. By providing first aid and using the appropriate bleeding control techniques, it is possible to save lives and reduce the risk of long-term health impacts.
The role of the bystander in bleeding control
The role of the bystander in bleeding control is to provide immediate first aid to the injured person and to seek additional medical help if necessary.
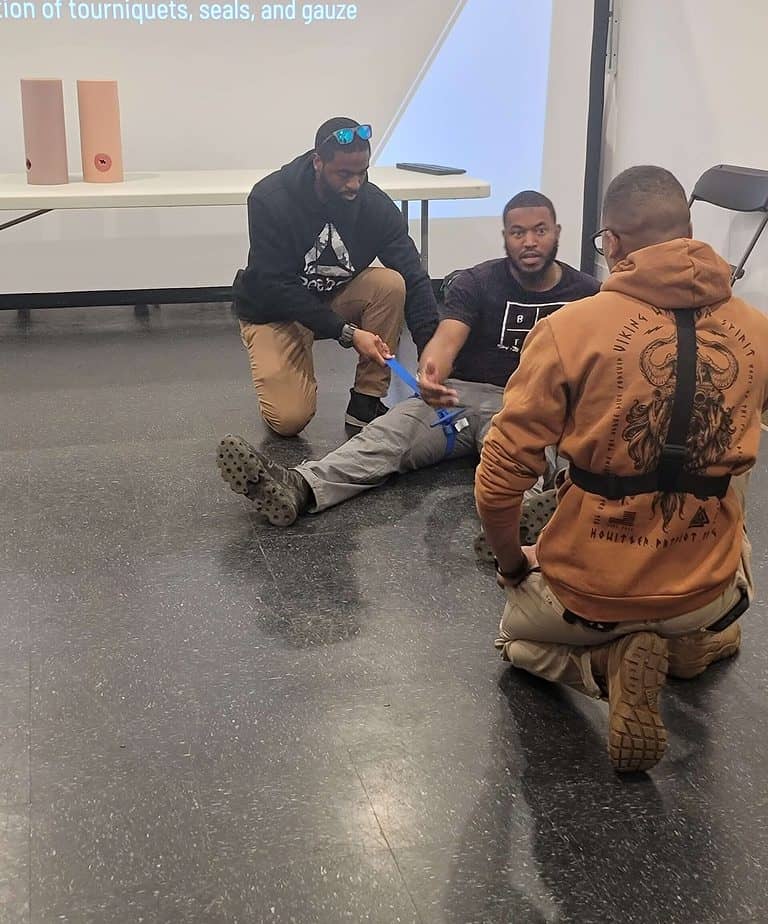

Here are some steps to follow when providing first aid for bleeding
Seek medical help: If the bleeding is severe and cannot be controlled, or if the person is in shock, call 911 or your local emergency number immediately.
Assess the situation: Check for any potential hazards and make sure it is safe to approach the injured person. Look for any obvious signs of injury, such as bleeding or obvious fractures.
Protect yourself: Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and a face mask, if available. This will help prevent the spread of infection.
Assess the severity of the bleeding: Determine whether the bleeding is minor or severe. Minor bleeding is usually controlled by pressure and can be managed with a bandage. Severe bleeding is characterized by a rapid loss of blood, which can lead to shock if not treated promptly. This type of bleeding requires more aggressive first aid measures, such as direct pressure or a tourniquet.
Control the bleeding: If the bleeding is minor, apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or bandage. If the bleeding is severe, consider using a tourniquet or applying direct pressure to the wound using your hands or a cloth.
It’s important to remember that providing first aid for bleeding is only a temporary measure until more advanced medical treatment can be obtained. If you are not trained in first aid, it is important to seek the help of a trained medical professional as soon as possible.
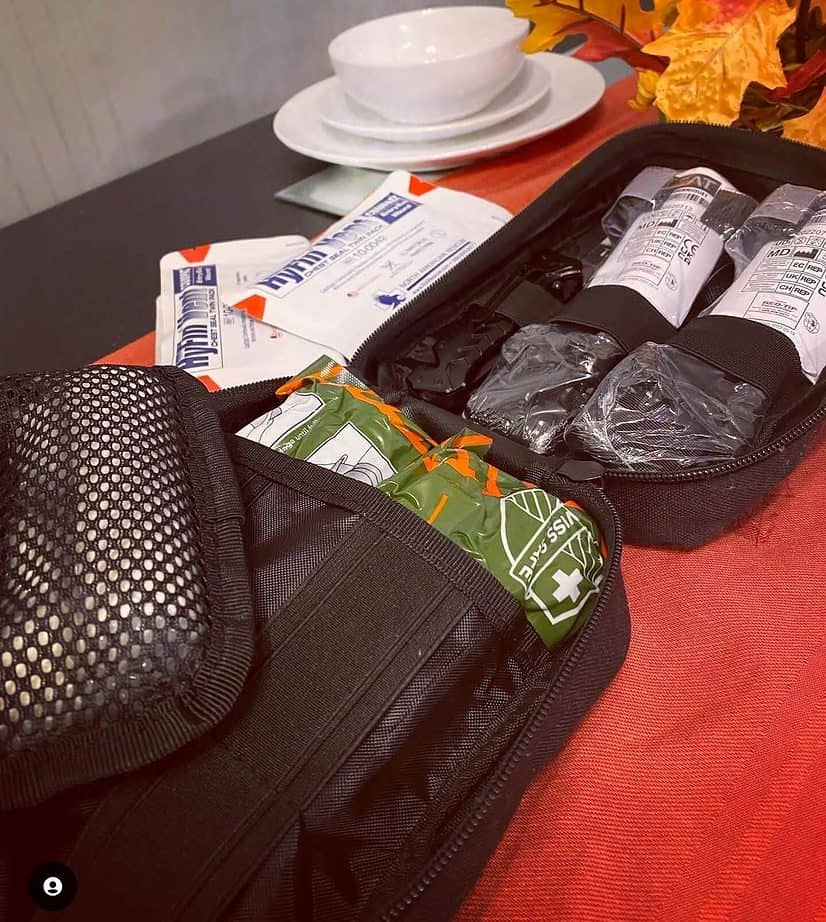
Types of bleeding control devices
Bleeding control devices are used to stop or reduce bleeding in the event of an injury. Here are some common bleeding control devices:
Tourniquets: A tourniquet is a device used to apply pressure to a limb in order to stop the flow of blood. Tourniquets are typically used in cases of severe bleeding, such as when a limb has been severely cut or amputated. They should only be used as a last resort, as they can cause tissue damage if left on for too long.
Compression bandages and dressings: Compression bandages and dressings are used to apply pressure to a wound in order to stop bleeding. These can be used for both minor and severe bleeding.
Hemostatic agents: Hemostatic agents are substances that are applied to a wound in order to promote blood clotting and stop bleeding. These agents come in various forms, including powders, gels, and pads. They can be used in combination with other bleeding control measures, such as compression or tourniquets.
It’s important to note that these devices should only be used by trained medical professionals or individuals who have received proper training in their use. In some cases, the use of these devices may be contraindicated, so it’s important to assess the situation and consult with a medical professional before using them.
How to use bleeding control devices

Tourniquet: A tourniquet is used to apply pressure to a limb in order to stop the flow of blood. It should only be used as a last resort, as it can cause tissue damage if left on for too long. To use a tourniquet, follow these steps:
Identify the location of the bleeding and position the tourniquet as high on the limb as possible; NOT as close to the wound.
Tighten the tourniquet until the bleeding stops.
Secure the tourniquet in place by tying it off or using the provided mechanism.
Note the time the tourniquet was applied.
Tourniquets are typically used in cases of severe bleeding, such as when a limb has been severely cut or amputated. They should be placed on the limb, above the wound and as close to the wound as possible.
Compression: Compression is used to apply pressure to a wound in order to stop bleeding. It can be used for both minor and severe bleeding. To use compression, follow these steps:
Identify the location of the bleeding and position a compression bandage or dressing over the wound.
Apply firm, steady pressure to the bandage or dressing using your hand or a compression device.
Secure the bandage or dressing in place using adhesive tape or a wrap.
Compression can be used on any part of the body where bleeding is present.
Chest seal: A chest seal is a device used to cover and seal a wound on the chest in order to prevent air from entering the chest cavity. It is typically used in cases of a punctured lung, also known as a pneumothorax. To use a chest seal, follow these steps:
Identify the location of the wound and position the chest seal over the wound.
Press the chest seal firmly onto the skin to create a seal.
Secure the chest seal in place using adhesive tape or a wrap.
Chest seals should only be used on wounds on the chest. They should not be used on wounds on other parts of the body.
The importance of proper training and practice
Proper training and practice are important in order to effectively use bleeding control devices and provide effective first aid for bleeding. Here are some reasons why proper training and practice are important:
Hands-on training with bleeding control devices: Hands-on training allows individuals to become familiar with the proper use of bleeding control devices and to practice using them in a controlled environment. This can help them feel more confident and prepared to use these devices in a real-life situation.
Staying up to date with current best practices: Best practices for first aid and bleeding control can change over time as new research becomes available. It’s important for individuals to stay up to date with current best practices in order to provide the most effective care possible.
Proper training and practice can help individuals feel more confident and prepared to provide first aid for bleeding in a real-life situation. It’s important to remember that providing first aid for bleeding is only a temporary measure until more advanced medical treatment can be obtained, and that individuals should seek the help of a trained medical professional as soon as possible if they are not trained in first aid.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hemorrhage control plays a crucial role in saving lives in emergency situations. The ability to quickly and effectively stop bleeding can mean the difference between life and death in many cases. That’s why it’s so important for individuals to be prepared and to know how to respond appropriately in the event of an injury or medical emergency.
Proper training and practice are key to being prepared for a bleeding emergency. Hands-on training with bleeding control devices, such as tourniquets, compression bandages, and hemostatic agents, can help individuals feel more confident and prepared to use these devices in a real-life situation. It’s also important to stay up to date with current best practices in order to provide the most effective care possible.
While providing first aid for bleeding is only a temporary measure until more advanced medical treatment can be obtained, it’s still an essential part of emergency care. By being prepared and knowing how to respond appropriately, individuals can potentially save lives in emergency situations.